Sports Science Weekly Gym Bag - 10-28-09
/The Overmanager: Why the New York Yankees' Joe Girardi is too smart for his own good
To play in the NFL, you have to make a show of going to college. To play in the NBA, you have to get through high school. To sign a contract with a major league baseball team, all you have to do is convince someone you're 16, provided you weren't born in a country with inconvenient labor laws. Perhaps this goes some way toward explaining both the high reverence in which the intellectual is held in baseball and the low standards necessary to qualify as one...
Running To The Right Beat
With the Fall marathon season in full swing, thousands of runners are gearing up for the big day. Just as important as their broken-in shoes and heart rate monitor is their source of motivation, inspiration and distraction: their tunes. Several recent studies try to chase down the connection between our ears and our feet...
Phys Ed: Do More Bicyclists Lead to More Injuries?
Recently, surgeons and emergency room physicians at the Rocky Mountain Regional Trauma Center in Denver noticed a troubling trend. They seemed to be seeing cyclists with more serious injuries than in years past. Since many of the physicians at the hospital, a Level I trauma center serving the Denver metropolitan area, were themselves cyclists, they wondered if their sense of things was accurate. So the doctors began gathering data on all cycling-related trauma admittances at the hospital and dividing them into two blocks, one covering 1995-2000 and the other 2001-6...
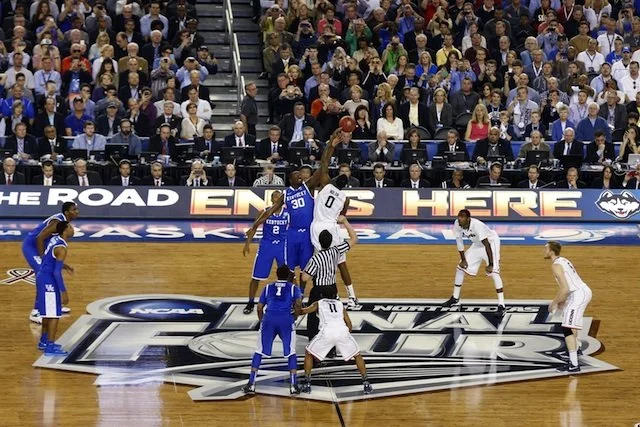
Football
In light of a recent post on the difficulty of changing our decision-making habits - even when we're aware that our habits are biased and flawed - I thought it might be interesting to look at two examples from professional football. Why sports? Given the intense competitive pressure in the NFL - there's a thin line between victory and ignominy - you'd expect head coaches to have corrected many of their decision-making mistakes, especially once those mistakes have been empirically demonstrated. But you'd be wrong.
Consider some research done by David Romer, an economist at UC Berkeley, who published a 2001 paper entitled "Do Firms Maximize? Evidence From Professional Football". The question Romer was trying to answer is familiar to every NFL fan: what to do on 4th down? Is it better to bring on the kicking team for a punt or field-goal attempt? Under what conditions should coaches risk going for it?
Missed Kicks Make Brain See Smaller Goal Post
Flubbing a field goal kick doesn’t just bruise your ego — new research shows it may actually change how your brain sees the goal posts. In a study of 23 non-football athletes who each kicked 10 field goals, researchers found that players’ performance directly affected their perception of the size of the goal: After a series of missed kicks, athletes perceived the post to be taller and more narrow than before, while successful kicks made the post appear larger-than-life. Professional athletes have long claimed that their perception changes when they’re playing well — they start hitting baseballs as large as grapefruits, or aiming at golf holes the size of a bucket — but many scientists have been slow to accept that performance can alter visual perception...
Baseball: Head-first Slide Is Quicker
Base running and base stealing would appear to be arts driven solely by a runner's speed, but there's more than mere gristle, bone and lung power to this facet of baseball -- lots of mathematics and physics are at play. Who gets there faster, the head-first slider or the feet-first?
Pump your arms to speed up your legs, thanks to “neural coupling”
“Keep pumping your arms!” That’s one of those canonical pieces of advice that it seems every coach gives to his or her runners. The idea is that, late in a run or race when your legs are burning and you’re starting to slow down, if you keep moving arms briskly, your legs will follow. It’s a nice idea — it’s always good to have some concrete piece of advice that you can hang onto when it seems like the world is about to explode. But does it work?
Unfortunately, I don’t know. But in the course of researching a completely different topic today, I stumbled on an interesting piece of research by Daniel Ferris, a University of Michigan researcher who’s best known for his research into assisted movement using robotic exoskeletons. The paper, which appeared in the journal Exercise and Sport Science Reviews back in 2006, is called “Moving the arms to activate the legs.” The full text is available here...
The Human Body Is Built for Distance
Does running a marathon push the body further than it is meant to go? The conventional wisdom is that distance running leads to debilitating wear and tear, especially on the joints. But that hasn’t stopped runners from flocking to starting lines in record numbers. Last year in the United States, 425,000 marathoners crossed the finish line, an increase of 20 percent from the beginning of the decade, Running USA says. Next week about 40,000 people will take part in the New York City Marathon. Injury rates have also climbed, with some studies reporting that 90 percent of those who train for the 26.2-mile race sustain injuries in the process...